创建简单 DAG 文件
DAG 文件示例
可以在主页查看到很多 DAG 示例文件,进入对应 DAG code 页面,可以看到对应的代码
当前编写一个简单的 DAG 文件, test_dag.py1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285# [START import_module]
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from textwrap import dedent
import os
import time
# The DAG object; we'll need this to instantiate a DAG
from airflow import DAG
# Operators; we need this to operate!
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator # 使用 PythonOperator
from airflow.models import Variable
from airflow.providers.postgres.operators.postgres import PostgresOperator
import psycopg2
from airflow.operators.email import EmailOperator
from airflow.providers.http.operators.http import SimpleHttpOperator
from airflow.providers.http.sensors.http import HttpSensor
import json
from airflow.operators.trigger_dagrun import TriggerDagRunOperator
# [END import_module]
# [START default_args]
# These args will get passed on to each operator
# You can override them on a per-task basis during operator initialization
default_args = {
'owner': 'airflow',
'depends_on_past': False,
'email': ['[email protected]'],
'email_on_failure': True, # 设置邮件失败也会发送
'email_on_retry': True, # 设置邮件重试也会发送
'retries': 2, # 重试次数
'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=5), # 重试间隔
# 'queue': 'bash_queue',
# 'pool': 'backfill',
# 'priority_weight': 10,
# 'end_date': datetime(2016, 1, 1),
# 'wait_for_downstream': False,
# 'dag': dag,
# 'sla': timedelta(hours=2),
# 'execution_timeout': timedelta(seconds=300),
# 'on_failure_callback': some_function,
# 'on_success_callback': some_other_function,
# 'on_retry_callback': another_function,
# 'sla_miss_callback': yet_another_function,
# 'trigger_rule': 'all_success'
}
# [END default_args]
def sum100():
sum = 0
for i in range(100):
sum += i
print(sum)
return sum # 测试 xcom 跨任务通信
# 获取 sum_1_100 的值,测试 xcom 跨任务通信
def get_sum100(**context):
sum_value = context['ti'].xcom_pull(dag_id='test_dag',task_ids='sum_1_100',key= "return_value")
#sum_value = context['ti'].xcom_pull(task_ids='sum_1_100', key= "return_value")
print(sum_value)
print('1+2+...+101=',sum_value+101)
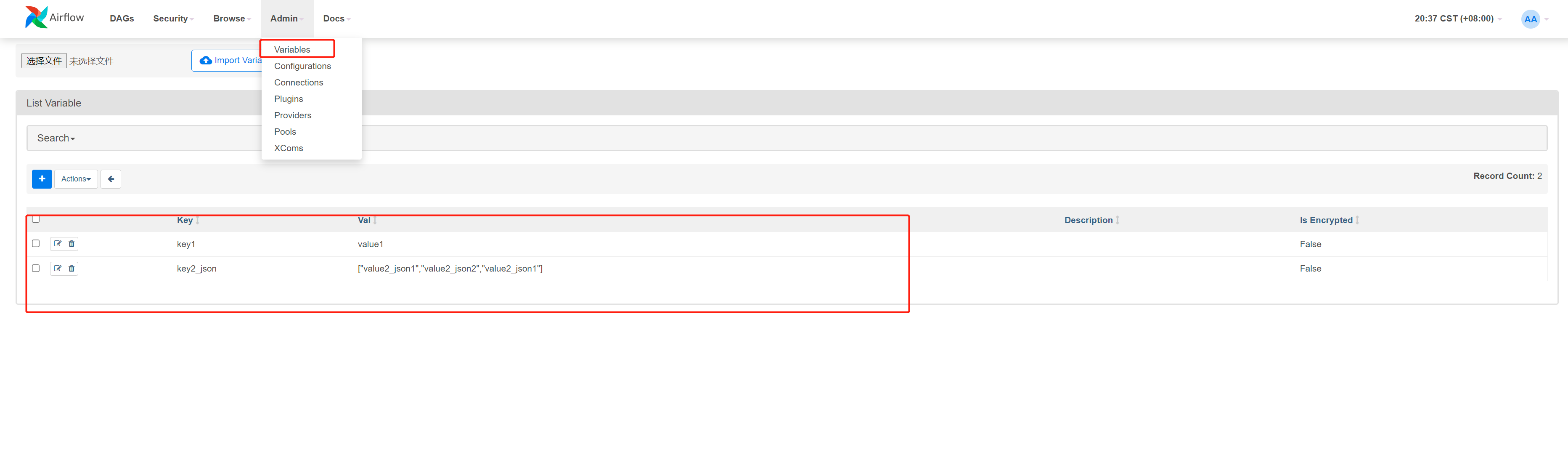
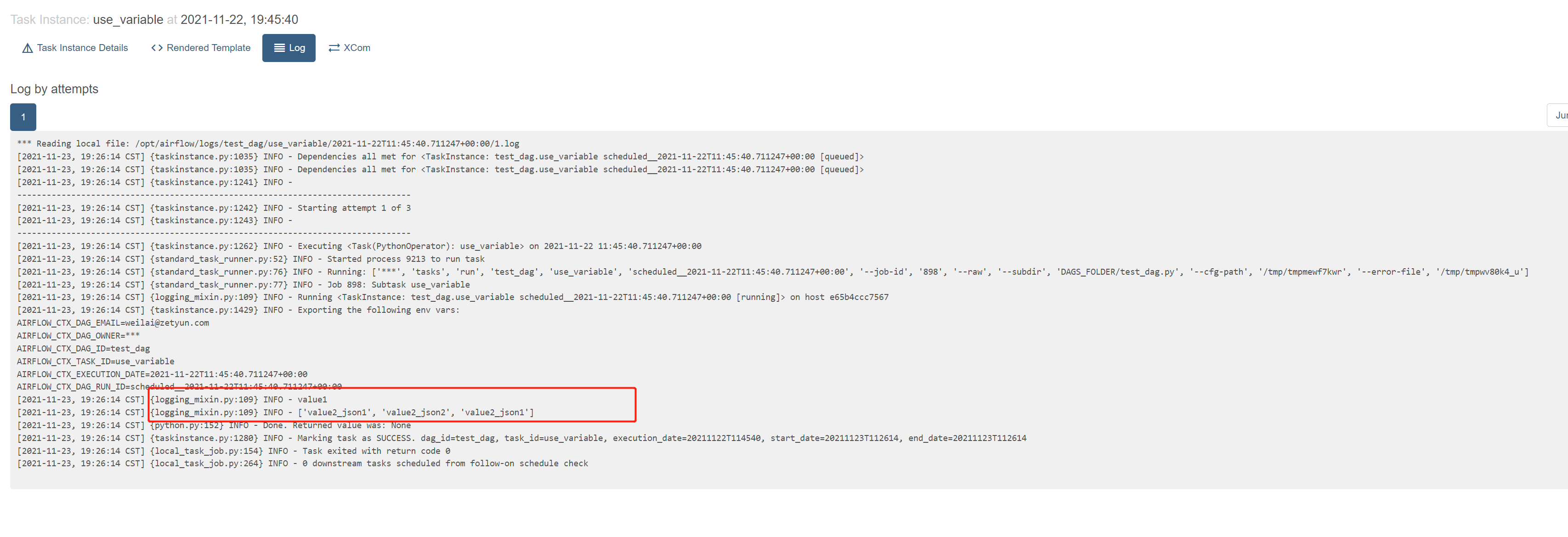
def use_variable():
# 需要在网页上配置 variable,以及导入包
variable_1 = Variable.get("key1")
variable_2 = Variable.get("key2_json", deserialize_json = True)
print(variable_1)
print(variable_2)
def run_with_config(**context):
config_value = context["dag_run"].conf.get("key")
value = 'not found config_value'
if config_value:
value = config_value
print(value)
def run_failed():
print('this task will fail')
print(1/0)
def use_pg_insert():
# 通过 hook 获取 connection 中保存的信息
from airflow.hooks.base_hook import BaseHook
conn = BaseHook.get_connection('airflow_pg')
print(conn)
pgdb = psycopg2.connect(
host=conn.host,
user=conn.login,
password=conn.password,
database=conn.schema,
port=conn.port
)
pgcursor = pgdb.cursor()
now_1 = datetime.now()
str_now_1 = now_1.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H%M%S')
now_2 = datetime.now()
str_now_2 = now_2.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H%M%S')
now_times_list = [str_now_1, str_now_2]
for now_time_str in now_times_list:
sql = f"""
INSERT INTO test(str_time) VALUES ('{now_time_str}')
"""
print(sql)
pgcursor.execute(sql)
pgdb.commit()
print(pgcursor.rowcount, "record inserted.")
pgdb.close()
def check(response):
if response == 200:
print("Returning True")
return True
else:
print("Returning False")
return False
def sleep_60s():
print('sleep 60s')
time.sleep(60)
print('sleep 60s finished')
def sleep_30s():
print('sleep 30s')
time.sleep(30)
print('sleep 30s finished')
# 测试此 task 运行完后,然后另一个 DAG 运行
def print_time_to_txt():
print('hello world')
os.system("echo $(date)-from_task_dag_print_time > /opt/airflow/logs/date.txt")
# [START instantiate_dag]
with DAG(
'test_dag', # DAG 的名字
default_args=default_args, # 使用的上面定义的基本变量
description='简单 DAG 示例', # DAG 的描述信息
schedule_interval='30 20 * * *', # 每天 20:30 运行一次
start_date=datetime(2021, 11, 15), # 开始时间
catchup=False, # 关闭补跑
max_active_runs = 1, # 同时只能进行 1个 任务执行
tags=['example'], # 标签
) as dag:
# [END instantiate_dag]
# t1, t2 and t3 are examples of tasks created by instantiating operators
# [START basic_task]
dag.doc_md = """
This is a documentation placed anywhere
""" # otherwise, type it like this
# [END basic_task]
# 需要引入 PythonOperator
sum100_task = PythonOperator(
task_id = "sum_1_100",
python_callable = sum100
)
get_sum_100 = PythonOperator(
task_id = "get_sum_100",
python_callable = get_sum100
)
print_time_to_text_task = PythonOperator(
task_id = "print_time_to_txt",
python_callable = print_time_to_txt
)
use_variable = PythonOperator(
task_id = "use_variable",
python_callable = use_variable
)
run_with_config = PythonOperator(
task_id = "run_with_config",
python_callable = run_with_config
)
# 测试重试次数和间隔
run_failed = PythonOperator(
task_id = "run_failed",
python_callable = run_failed
)
use_pg_insert_task =PythonOperator(
task_id='use_pg_insert',
python_callable=use_pg_insert,
)
# 需要引入 PostgresOperator ,并且在网页中 admin/connections 中配置好连接信息
pgsql_file_task = PostgresOperator(
task_id='pgsql_file_task',
postgres_conn_id='airflow_pg',
sql='test_update_id1.sql', # ./dag 目录下
dag=dag,
)
# 需要引入EmailOperator ,并且正确配置邮件信息
email_task = EmailOperator(
task_id = "send_email",
to='[email protected]',
subject='DAG TEST - {{ds}}', # 测试 jinja_templated
html_content="""
<h3>Email Test</h3> {{ ds_nodash }}<br/>{{ dag }}<br/>{{ conf }}<br/>{{ next_ds }}<br/>{{ yesterday_ds }}<br/>{{ tomorrow_ds }}<br/>{{ execution_date }}<br/>
""",
dag=dag
)
# 使用 HttpSensor 和 SimpleHttpOperator 测试 sensor 功能以及 provider
task_http_sensor_check = HttpSensor(
task_id='checkuser_from_httpsensor',
http_conn_id='http_default',
method='GET',
endpoint='api/v1/users/httpsensor',
response_check=lambda response: True if check(response.status_code) is True else False,
poke_interval=5,
dag=dag,
)
task_sleep_60s =PythonOperator(
task_id='task_sleep_60s',
python_callable=sleep_60s,
)
task_sleep_30s =PythonOperator(
task_id='task_sleep_30s',
python_callable=sleep_30s,
)
task_adduser_from_api = SimpleHttpOperator(
task_id='adduser_from_api',
method='POST',
endpoint='api/v1/users',
data = json.dumps(
{
"email": "[email protected]",
"first_name": "httpsensor",
"last_name": "httpsensor",
"roles": [
{
"name": "Public"
}
],
"username": "httpsensor",
"password": "httpsensor"
}
),
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json"},
dag=dag,
)
task_deluser_from_api = SimpleHttpOperator(
task_id='deluser_from_api',
method='DELETE',
endpoint='api/v1/users/httpsensor',
headers={"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"},
dag=dag,
)
# 测试通知 下一个 DAG 运行
trigger_next_dag = TriggerDagRunOperator(
trigger_dag_id = "after_print_time_to_txt",
task_id = "get_time_txt_from_test_dag",
wait_for_completion =False # 只通知运行,不等待运行结果
)
sum100_task >> get_sum_100 >> email_task # 任务 sum100_task 执行完后执行 get_sum_100
use_pg_insert_task >> pgsql_file_task >> email_task
task_sleep_60s >> task_adduser_from_api >>task_sleep_30s >> task_deluser_from_api
print_time_to_text_task >> trigger_next_dag
# [END tutorial]
详细信息
正常情况下,一个 DAG 最好只运行一组相关的任务。此 DAG 仅作测试
导入的包和基本变量
一般最好写在 任务导入的地方, 此处先把所有的 导入的包展示
1 | # [START import_module] |
测试 xcom 跨任务通信
一个任务的值,另一个任务可以获取
1 | def sum100(): |
查看日志,有获取到值
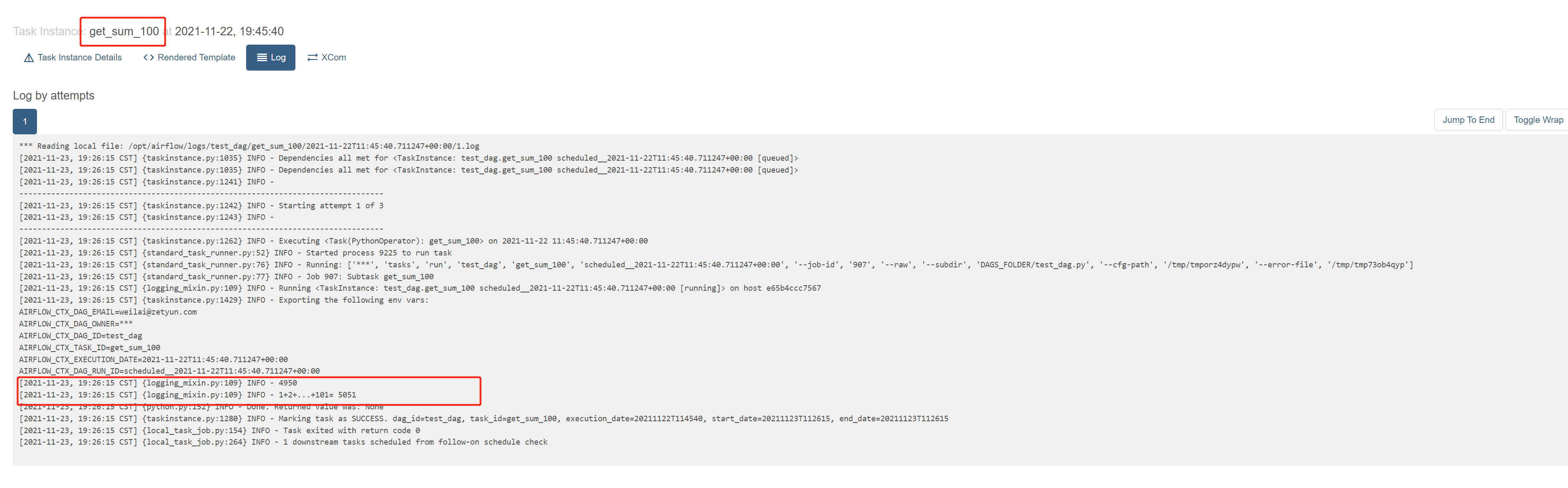
查看页面,也有显示

测试全局变量
1 |
|
定义的 variable 页面
查看日志,有获取到值
测试运行任务时传参
1 | def run_with_config(**context): |
未传入参数时
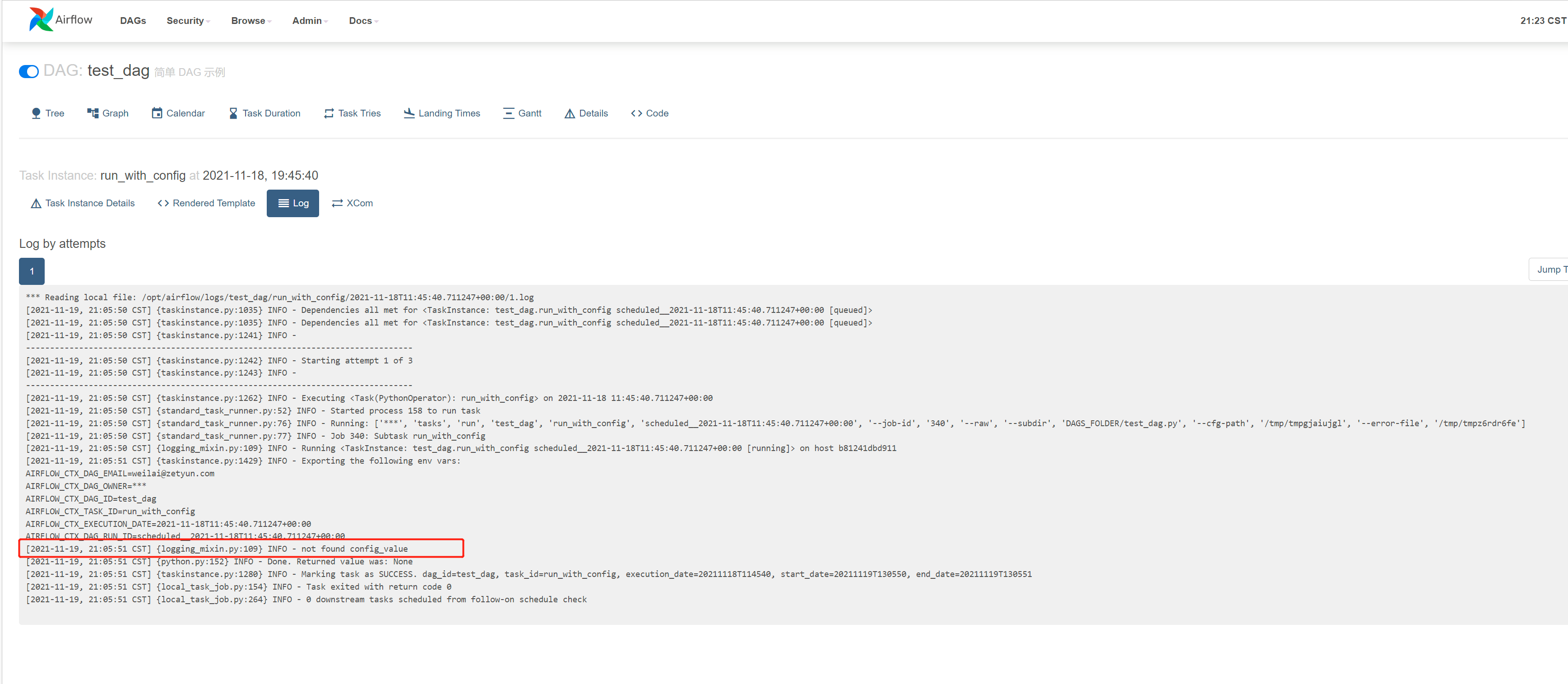
传入的参数
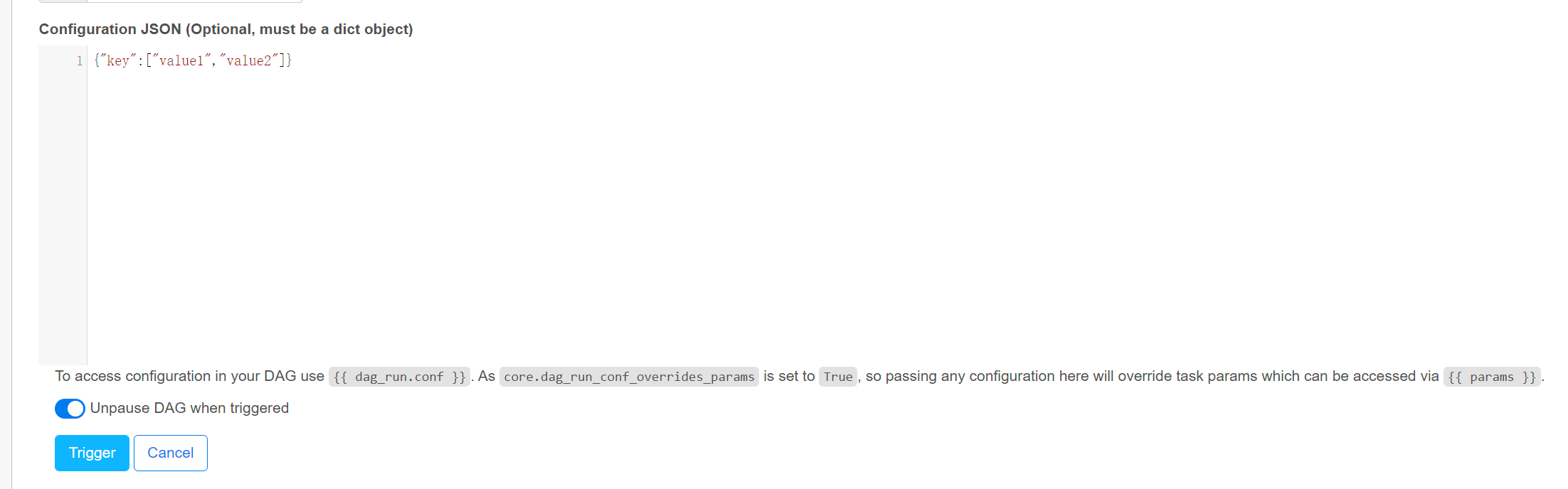
获取到传入的值

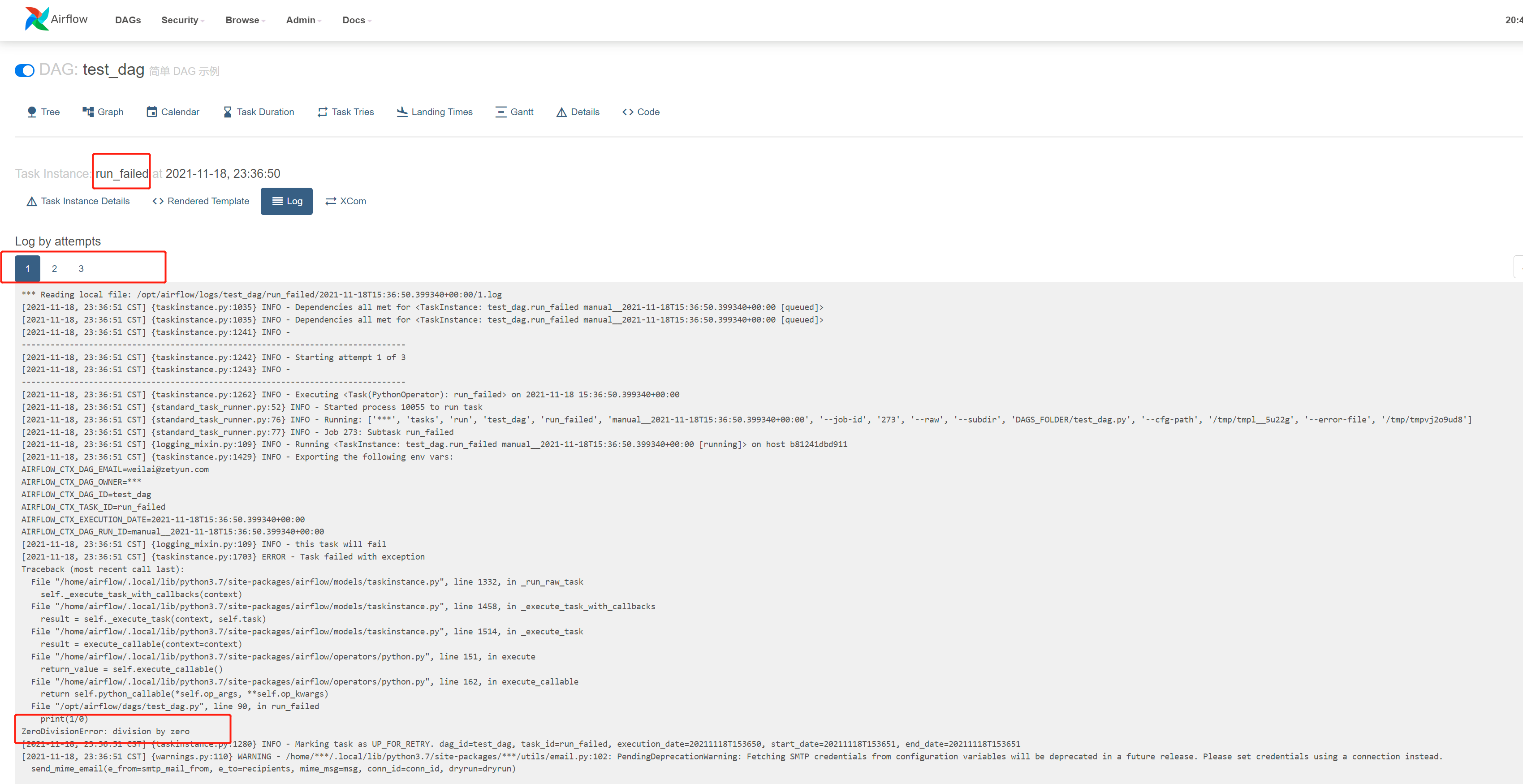
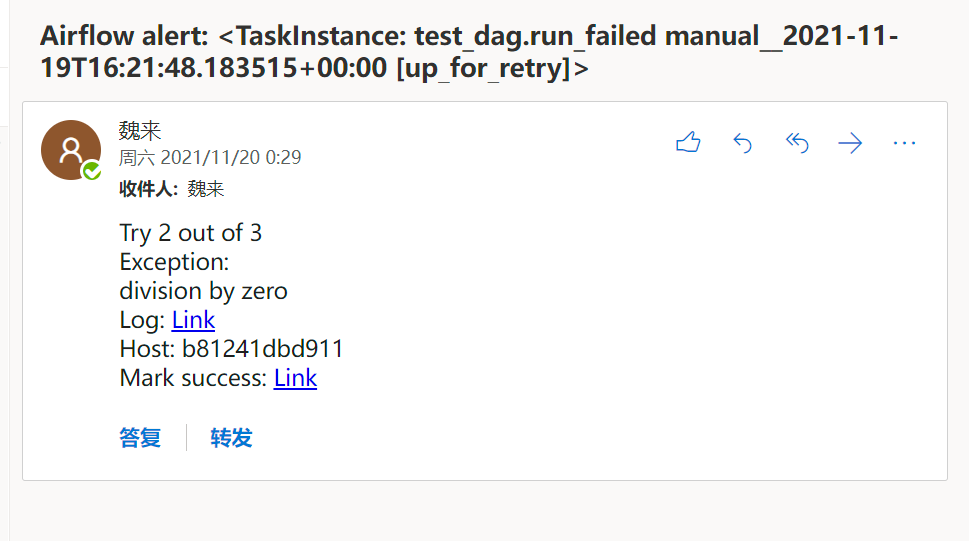
测试失败的任务
主要测试 retry 次数
1 | def run_failed(): |
根据定义重试了2次,
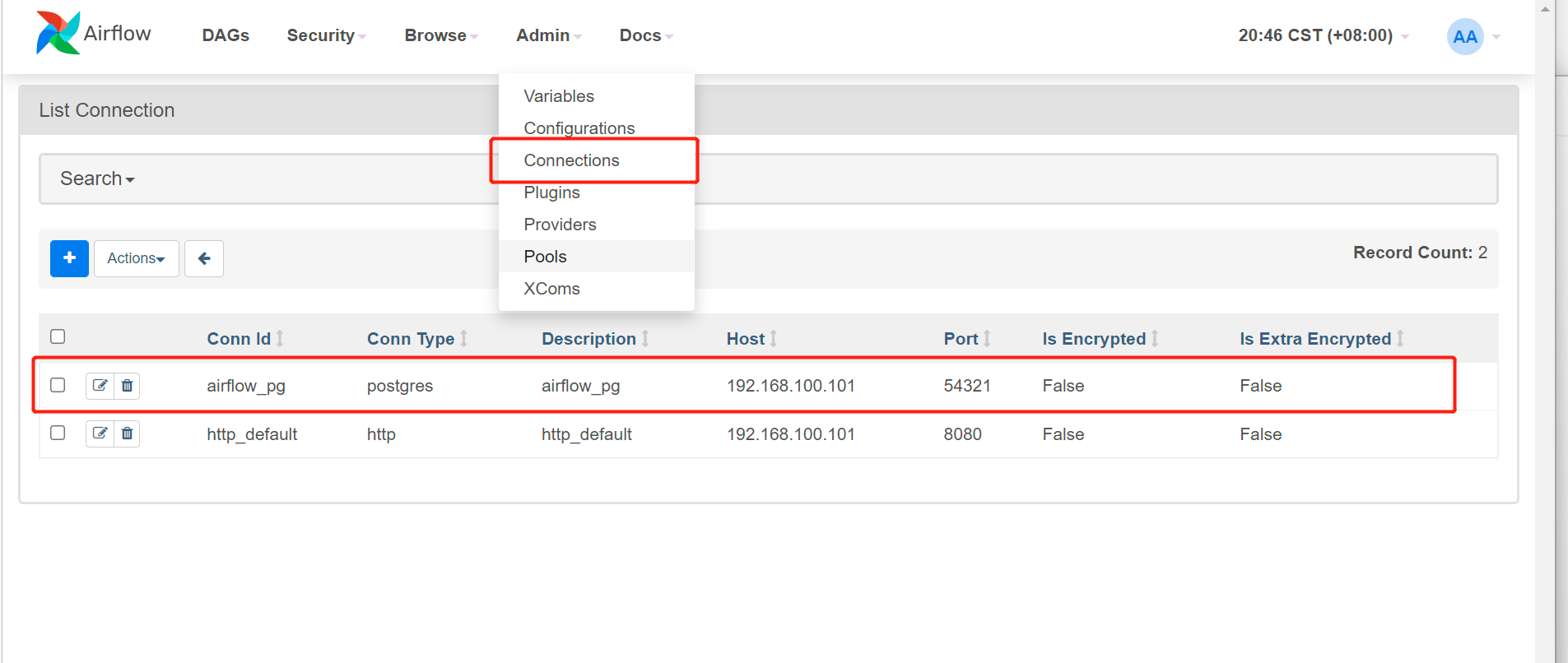
测试获取connections 信息
1 | def use_pg_insert(): |
获取 连接信息
查看已插入信息
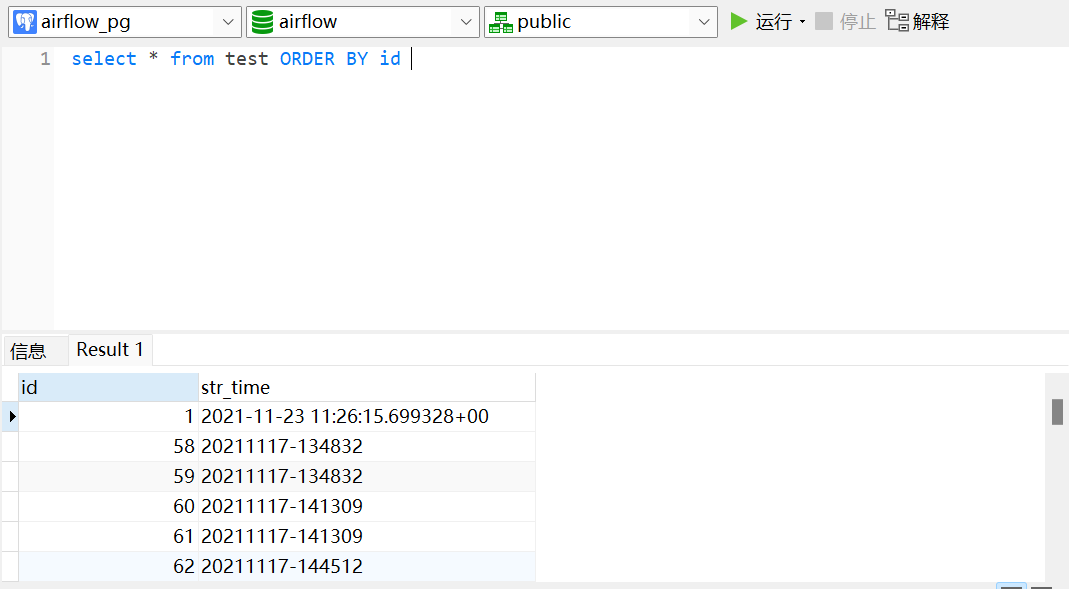
同时可以看到 id=1 的值 被修改
测试 PostgresOperator
1 | # 需要引入 PostgresOperator ,并且在网页中 admin/connections 中配置好连接信息 |
test_update_id1.sql 路径在 ./dag 下
1 | update test set str_time = now() where id = 1 |
id = 1 的值已被修改

测试发送邮件,以及templating-with-jinja
1 | # 需要引入EmailOperator ,并且正确配置邮件信息 |
使用了 jinja_templated,详细可参考 https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/tutorial.html#templating-with-jinja
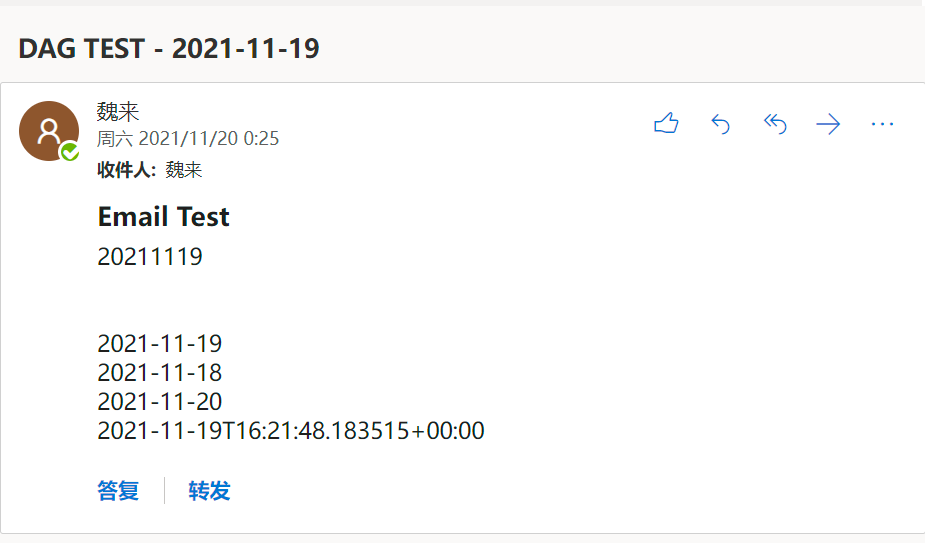
定义的失败也发送邮件
测试 sensor 功能以及 provider
使用 HttpSensor 和 SimpleHttpOperator 测试 sensor 功能以及 provider
task_http_sensor_check : 每 5s 监控 是否有 httpsensor 用户信息
60s 后,创建用户 httpsensor ,30s 后, 然后删除用户 httpsensor
1 | from airflow.providers.http.operators.http import SimpleHttpOperator |
可以查看到每隔 5秒观察一次,直到成功
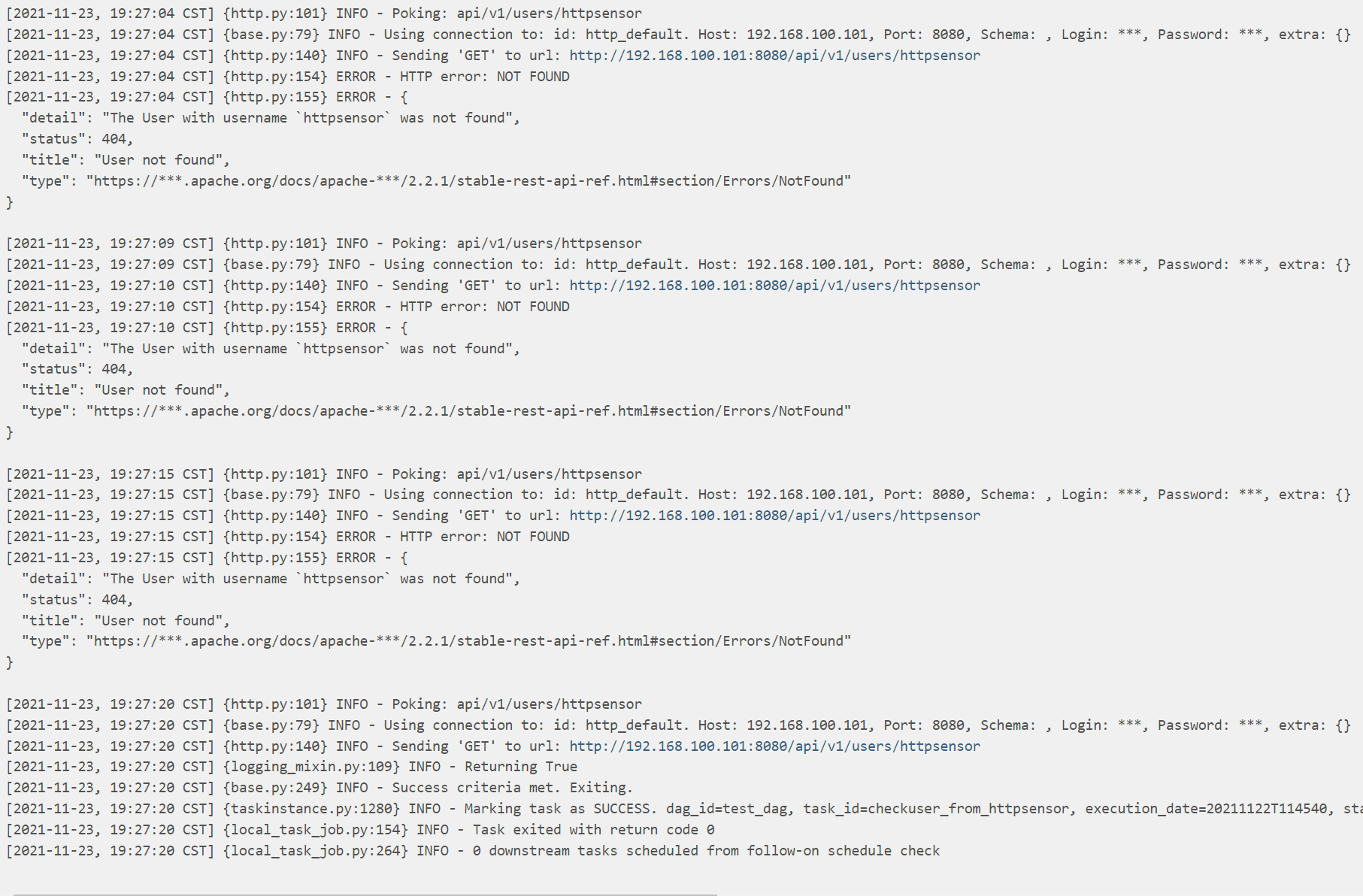
刚好这个时间点 创建用户 httpsensor
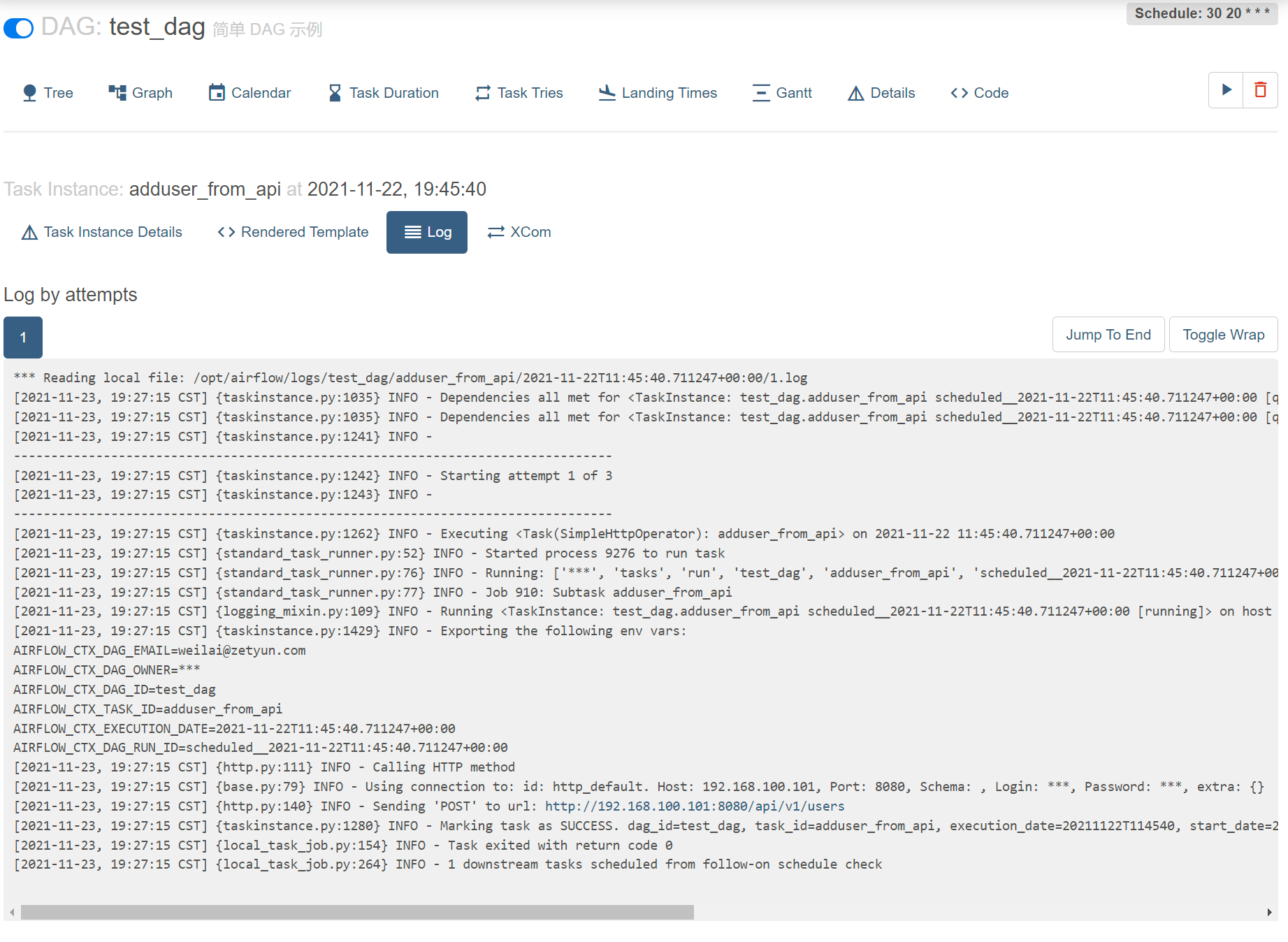
30s 后删除用户
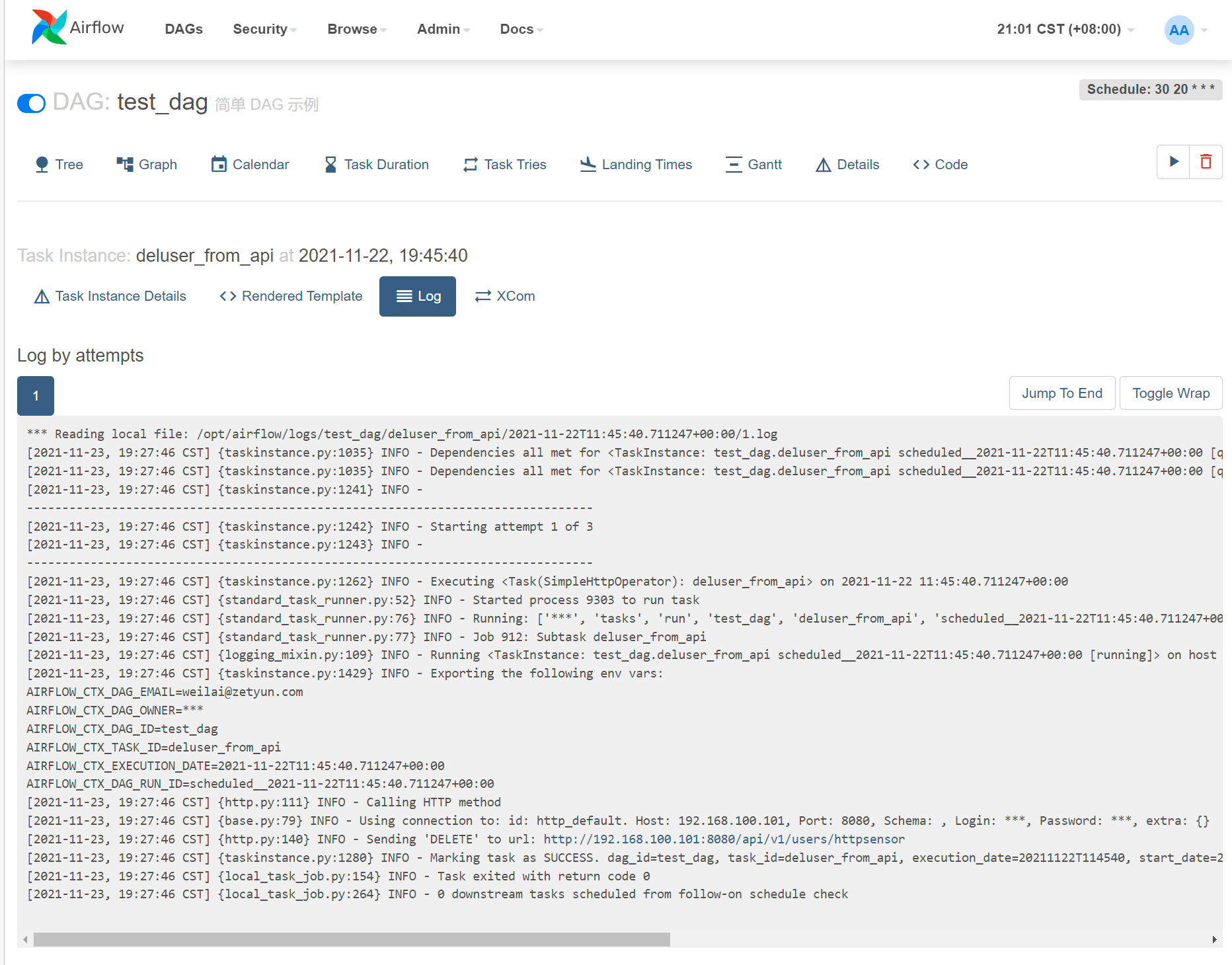
测试此 task 运行完后,然后通知另一个 DAG 运行
此 task 运行完后,然后通知另一个 DAG 运行
1 | def print_time_to_txt(): |
其中 after_print_time_to_txt.py DAG 文件如下
1 | from datetime import datetime, timedelta |
通知下一个DAG时间
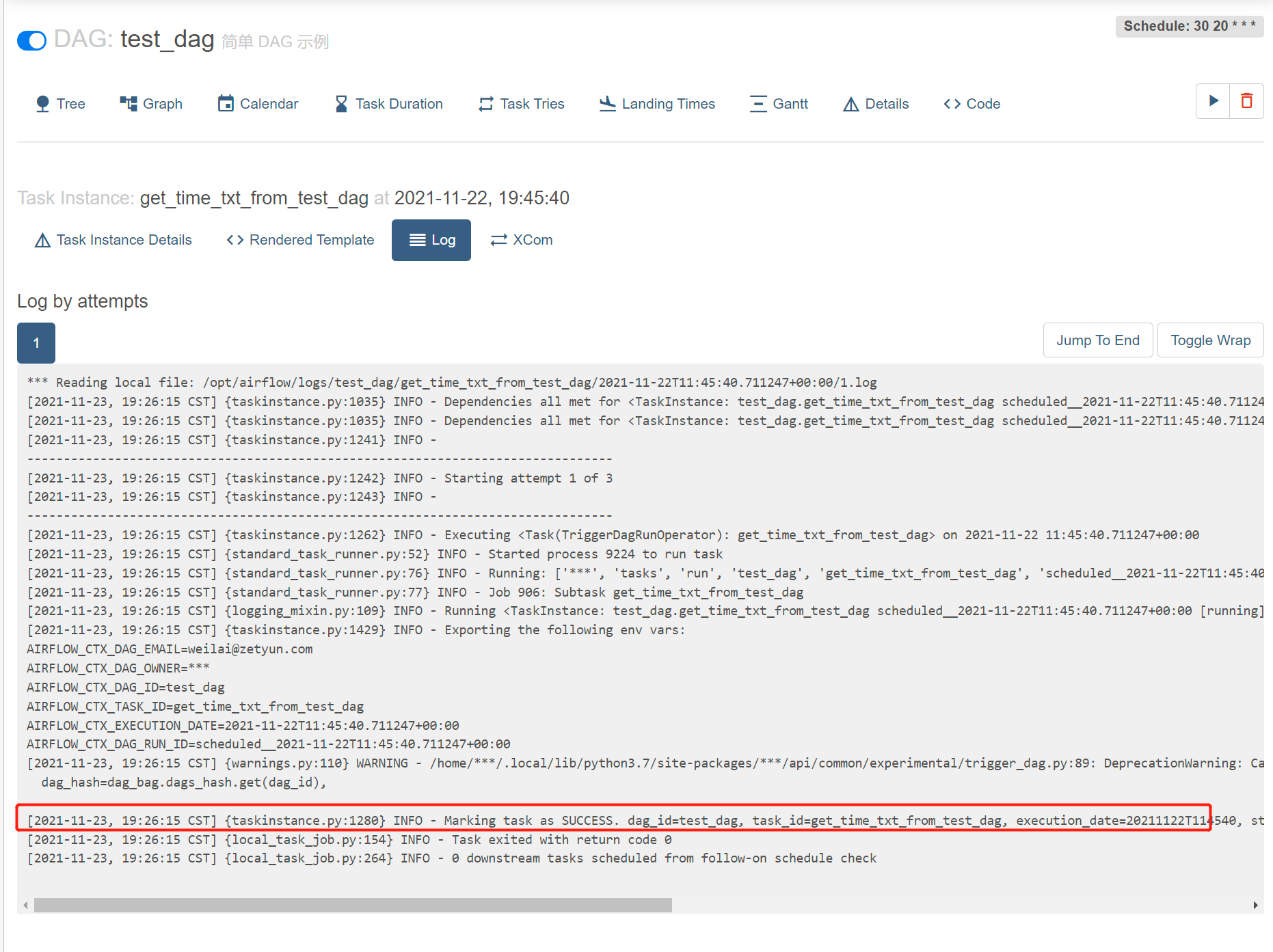
下一个DAG运行时间
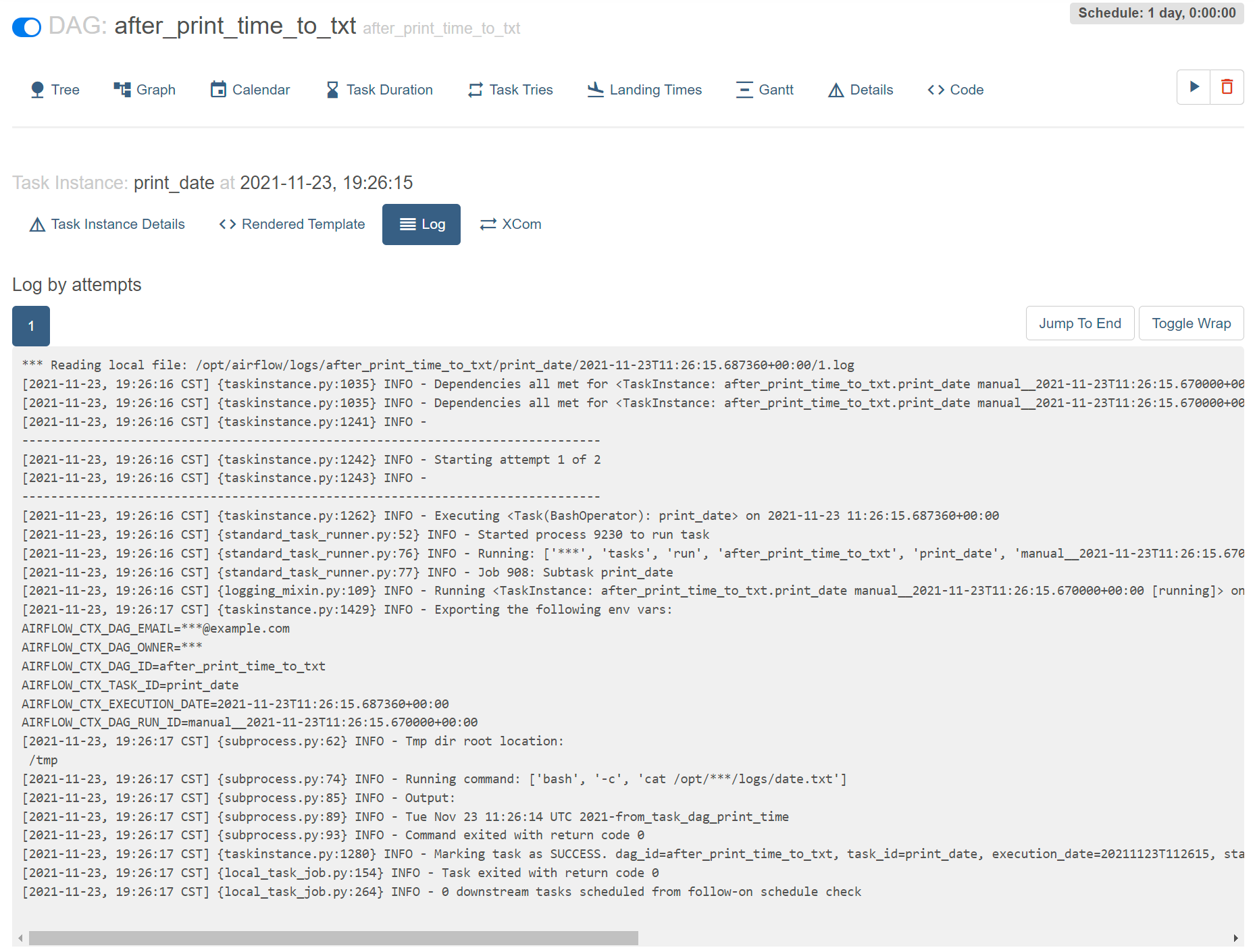
测试sensor, 观察到 test_dag 运行完后,再运行 watch_print_time_to_txt.py
watch_print_time_to_txt.py 内容如下
1 | from datetime import datetime, timedelta |
不停观察务开始5分钟前的test_dag
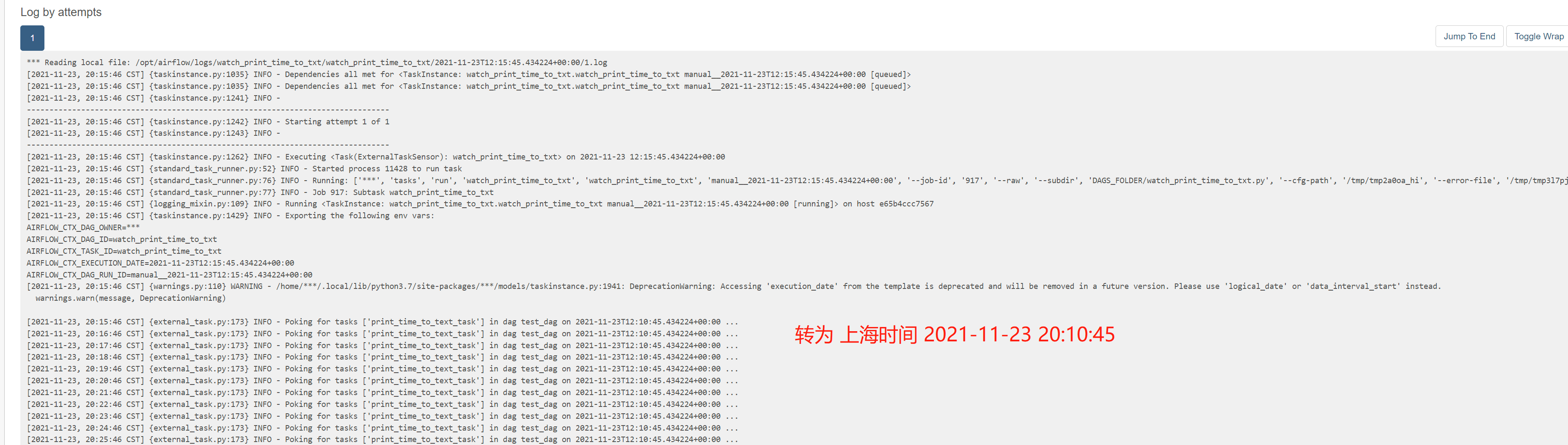
测试 Dynamic_DAG
一个 python 文件,生成多个 DAG 文件
1 | from airflow import DAG |
可以的看到 生成了 多个 DAG
写完保存到 ./dag 文件夹下可以被定时扫描到,并且可在 code 界面上详细查看